- What Exactly is Data Governance?
- Why Has Data Governance Become So Important?
- 7 Key Components of a Data Governance Framework
- What Are Common Data Governance Challenges?
- Establishing Effective Data Governance at Your Organization
- Best Practices for Data Governance Success
- Looking Ahead: The Future of Data Governance
When people hear the term “data governance,” they envision complex technical processes managed exclusively by IT personnel.
The concept of data governance is broader than technology – it is a company-wide framework for managing data from acquisition to disposal, depending on its purpose.
Furthermore, it is only partially internal. As the name suggests, data governance is an interpretation of a company’s internal data use, as well as a reflection of data regulations released by governments.
What Exactly is Data Governance?
Data governance is a set of rules and procedures that help make sure your data is accurate, secure, and used responsibly. Think of it as quality control for your company’s data.
At its core, data governance helps ensure that data is actionable and standardized to streamline data processing and ensure there are no issues in the data.
Data must drive your decisions and actions. With data governance measures in place, it will be easier to base your choices on trustworthy and actionable data.
That’s why data governance oversees how data is managed and used across the organization through policies, roles, metrics, and processes.
Data governance also breaks down silos so that everyone can leverage data to extract value while still maintaining security, privacy, and regulatory compliance.
It enables data-driven decision-making by establishing trust in data through traceability and quality. Here’s a simple way to think about it:
- Data management focuses on technology and databases
- Data quality focuses on accuracy and completeness
- Data governance connects them, providing coordination and standardization
In summary, data governance oversees and orchestrates how all data is managed to create business value. It provides the foundation for managing data as a true strategic asset.
Why Has Data Governance Become So Important?
With the exponential growth in data from new technologies like IoT sensors, social media, and mobile devices, the volume, variety, and velocity of data is massive.
This “big data” brings enormous potential but also complex challenges in how to manage it. At the same time, companies face growing regulatory compliance requirements around data security, privacy, and retention – from regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
On top of that, mergers, acquisitions, and modern cloud data platforms drive the need to integrate disparate data systems.
The result is a complex web of siloed, distributed data needing more oversight and governance, which leads to issues like:
- Inconsistent data across systems
- Unclear data ownership and usage policies
- Poor data quality
- Security and compliance risks
These issues prevent companies from unleashing the value of their data. This growing “data crisis” is precisely what data governance aims to solve.
7 Key Components of a Data Governance Framework
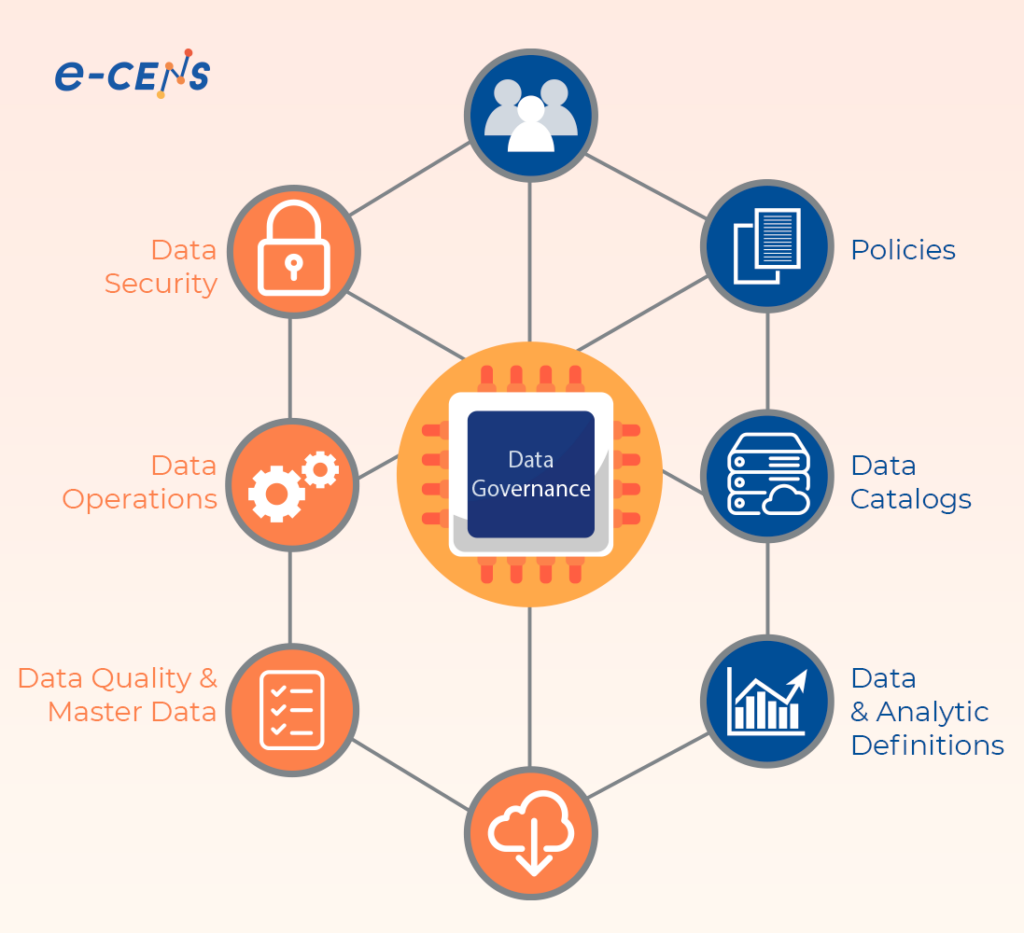
Implementing data governance involves connecting people, processes, and technology across the organization. While every company’s structure is unique, most data governance frameworks include these core components:
- People – Data governance professionals, data stewards, data owners, and other key IT staff are critical for overseeing policies, processes, and data lifecycles.
- Processes – Data governance involves many processes like issue and defect tracking, data quality monitoring, data lineage mapping, and more.
- Policies – Rules for proper data usage, sharing, security, retention, and deletion.
- Standards – Technical data storage, formats, metadata, schemas, and integration standards.
- Rules – Constraints and requirements for how data is managed.
- Security – Protection of data from unauthorized exposure or modification.
- Management – Data governance manages data during acquisition, storage, usage, archiving, and deletion. It covers the full lifecycle. Proper data governance allows organizations to trust their data, use it effectively, get value from it, and manage risks associated with data. It provides the foundation for managing data as an enterprise asset.
What Are Common Data Governance Challenges?
While the benefits are substantial, implementing effective data governance takes work. Based on our experience, these are some of the top challenges companies face:
- Data silos – Disjointed data stored in departmental silos makes governance difficult. A lack of data integration impedes governance.
- Poor data quality – Inaccurate, incomplete, or inconsistent data makes governance problematic. Resolving data quality issues is key.
- Lack of transparency – Undocumented data and opaque lineage hides potential problems. Data mapping provides the transparency needed for governance.
- Unsecure environments – Data spread across systems with weak access controls creates vulnerabilities. Securing data environments enables governance.
- Lack of data oversight – Without policies, processes, and accountable roles, data can easily get out of control. Oversight is critical.
- Change management – Getting user buy-in and adapting processes can require significant change management efforts. Overcoming these challenges requires executive sponsorship, user engagement, starting small, and implementing data governance iteratively.
Establishing Effective Data Governance at Your Organization
Now that you know what’s data governance and why it’s important to have it in your organization, comes the question of how do you implement it.
We’ll break it down for you step by step, and the first thing you need to think about is how this will help my organization grow…
Build a Business Case
The first step is building a solid business case. Data governance often gets positioned as just a compliance exercise, diminishing its value. Instead, make the case in business terms:
- How will it improve analytics and decision-making by enabling trust in data?
- What cost savings can be realized through better quality and fewer errors?
- How will it reduce risks related to security and privacy?
- What problems will it solve for business users that lack governed data today? Make the benefits tangible in terms of top leadership priorities.
- Link governance to digital transformation, customer experience, efficiency gains, risk reduction, and agility. With data increasingly driving competitive advantage, the case becomes very compelling.
Start with a Data Assessment
Once sponsorship is secured, perform an assessment focused on high-priority data domains. Document how this data is used, its value, risks and liabilities, and known quality issues. Quantify costs and risks where possible. Interview business stakeholders to capture pain points. This assessment validates where to focus initial governance efforts for maximum impact.
Define a Target Data Governance Operating Model
Next, outline the policies, processes, metrics, organization, and technology foundation required for governing priority data.
Define key roles and responsibilities. Document target processes for issue escalation, policy management, stewardship, and quality management.
Start by codifying existing controls and procedures, then identify enhancement opportunities. Performing this foundational design upfront helps avoid missteps.
Launch a Pilot Program
With the target model defined, start small by piloting governance on a subset of data. For example, kick-off efforts for customer data or product data.
Assign data owners and stewards. Implement process changes manually at first. Measure progress with a scorecard based on compliance, quality, risk, and value metrics.
Capture lessons learned and refine the processes and org model. Gradually expand the pilot across more data domains once the approach is proven.
Invest in Data Governance Software
As pilots demonstrate value, invest in enabling automation, reporting, and sustainability technologies. Mature capabilities like data discovery, lineage, policy management, stewardship workflows, and issue tracking avoid relying on complex manual oversight.
Integrating these data governance tools with your technology stack embeds controls into the environment. Leveraging this software also provides scalability as the program expands.
Institutionalize Data Governance
Finally, work towards making data governance an institutional capability at your organization. Incorporate training into onboarding processes.
Develop career paths for data stewards and governance leaders. Update company policies and procedures to include data governance requirements.
Report to executives on metrics tied to strategic KPIs. Continuously evaluate and enhance the program. This establishes data governance as a critical discipline.
While becoming a data-driven company requires change, those able to harness the value of their data responsibly will gain real competitive advantages.
Best Practices for Data Governance Success
- Get executive support – Sponsorship from leadership helps provide resources and aligns governance with strategic priorities.
- Start small – Begin with a limited scope, focusing on high-value data like customer data. Expand scope over time.
- Focus on business needs – Ensure governance policies and processes map to business requirements and priorities.
- Assign ownership – Data owners must be accountable for managing specific data domains or datasets.
- Develop data strategy – Define policies and roadmap aligned to use cases for analytics, reporting, compliance, etc.
- Monitor metrics – Track progress through KPIs for data quality, policy compliance, issue resolution, etc.
- Communicate benefits – Share successes and value from data governance to gain ongoing user buy-in.
- Automate where possible – Leverage tools for data discovery, lineage, policy enforcement, and stewardship.
- Make iterative improvements – Continuously evaluate issues and enhance processes to expand governance.
Data governance is an evolving, collaborative process. Starting small, demonstrating value, and making ongoing enhancements can have a big impact on maximizing benefits and minimizing risks from data.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Data Governance
Given today’s exponential data growth, data governance will become even more critical. Here are a few key trends to watch:
- Increasing regulatory compliance mandates will necessitate greater data security, privacy, and retention controls. Standards like GDPR are early signs of this heightened regulatory environment.
- New analytic techniques like AI and machine learning will emphasize data quality, consistency, and contextualization through governance. Garbage in, garbage out!
- Business self-service and democratization of data access will change demands on governance programs. Broader usage means simpler metadata, more automation, and greater emphasis on data literacy.
- IoT, social media, and other new data sources will explode data volumes and increase the need for governance to tie these new inputs together.
- Cloud data platforms and hybrid environments will require evolving governance to stretch across on-prem and multi-cloud systems.
To harness these trends and the explosive increase in data, companies must take a strategic approach to data governance.
Those that do will gain a competitive advantage through trusted data assets. Those that don’t will find themselves lost in a sea of complex, unusable information.
After seeing how data governance has matured over the past decade, I’m confident its importance will grow.
Companies that invest now to build robust governance will see massive dividends over the long term.
If you need help setting up a data governance framework for your company, we’re happy to help you!
At e-CENS, we have more than 20+ years of experience in the digital landscape, helping clients achieve their targeted growth objectives using data science and analytics.
Do You Have a Data Governance Framework Set up?
Invest Now in Building a Strong Governance and Secure Yourself Massive Dividends in The Long Run!




