Key Takeaway
According to Google, they’ll NOT be phasing cookies out in the second half of Q4 2024!
Overview of browser cookies
Over the years, cookies have been in hot milk, but recently, with privacy concerns, they found themselves in hot water with regulators rather than grandmoms.
The EU, with its GDPR, the CCPA, and other privacy laws that protect users on the internet, have targeted cookies as a part of their crackdown. While using your web browsers to surf the internet, you must’ve pumped into those consent and cookie banners.
But what are those? Are cookies going away? How can you, as a professional marketer, keep track of customers and make targeting them more effective on a cookieless internet? That’s what we’re answering today in this blog.
What are browser cookies?
The modern internet wouldn’t be what it is now without them, and they go by multiple names, HTTP cookies, browser cookies, or just cookies.
Cookies are small pieces of data that websites store on a user’s browser. They play a crucial function as they remember user’s interactions with the website, such as login credentials, preferences, shopping cart items, and browsing history. They can also be used to track and analyze user behavior on websites.
So if a user leaves the website and returns, his information would be stored so he could proceed from where he left off, simply and seamlessly.
But like regular delicious cookies, they expire after some time. If they’re session cookies, they’ll be deleted when the browser is closed. They can also be manually deleted, which is the process we call clearing the cookies.
But, while cookies typically don’t store sensitive data like personal information and passwords, they could be used to track users on the internet, even over different websites, which landed them in hot water.
That’s why you’ll see those banners on almost every website, in different shapes and forms, but they’re everywhere.
How do browser cookies work?
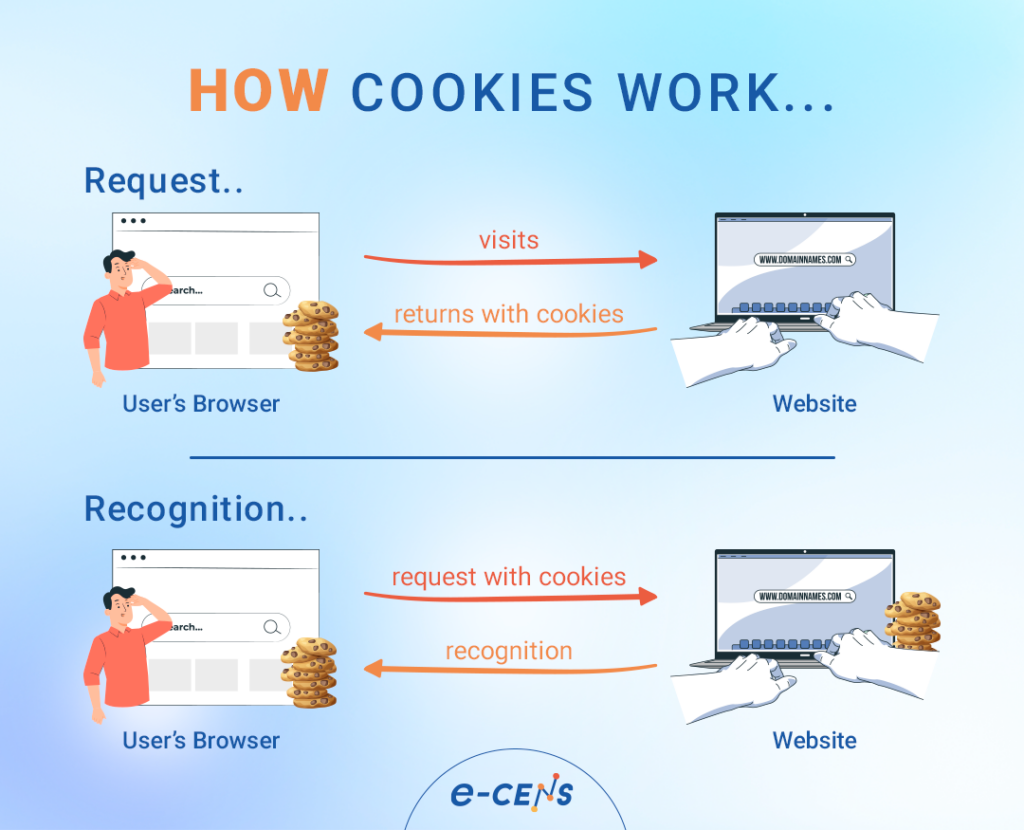
Once you’ve visited a website, they store a cookie on your website. As we’ve discussed, it’ll keep track of your interactions and information, and on leave, it’ll stay put until you come back, and it refreshes its data or expires if you don’t come back.
5 Types of cookies
Now, let us break down the different types of cookies that you might’ve heard about and which ones are going away!
1. Session cookies
These cookies, also known as transient cookies, are temporary cookies stored in the computer’s memory until the web browser is closed.
They don’t last for more than a session. Once the browser is closed, they’re gone, and that’s why they’re privacy-friendly.
If you ever went to an e-commerce shop without logging in and added some items to your cart, then closed the tab and came back, they’ll be there, but if you closed the browser, they’re gone.
2. Persistent cookies
These cookies, sometimes called permanent cookies, are a type of cookie that doesn’t get deleted once the browser is closed, like session cookies.
They last for a specific amount of time, days, months, or even years.
Have you logged into a website or a tool and clicked “remember me”? That’s persistent cookies in action.
3. Authentication cookies
Web servers use these cookies to know whether the user is logged in and with which account they are logged in.
These cookies pose a vulnerability as they could be stolen by a cyber criminal to gain unauthorized access to accounts, as happened with the famous YouTuber LinusTechTips, whose channels were hacked this way.
4. First-party cookies
First-party cookies are cookies that are set by the domain of the website that the user is visiting.
These cookies vary in nature. Some are session cookies, deleted after the browser is closed, while others are persistent cookies, which remain on the user’s device for a set period.
5. Tracking cookies / third-party cookies ????
These are a type of cookie that gets placed on a user’s hard disk by a website different than the one they’re visiting, and that’s why advertising networks commonly use them.
These cookies get targeted by regulations because they pose a privacy risk for the users.
So, if you’ve ever browsed for a product on one site and then seen ads for that product on a different site, it’s likely that tracking cookies were involved.
And those cookies are going away in 2024. With its Google Chrome browser, Alphabet will join Mozilla Firefox in omitting the use of cookies, the 3rd party cookies to be exact, so the question becomes, what do in a cookieless world?
How do you thrive on a cookieless internet?

Let me say this: the internet isn’t going cookieless.
Third-party cookies will be phased out in Q4 2024. Check Google’s announcement here.
But first-party cookies are not going anywhere. Google aims to block invasive tracking technologies like third-party cookies and replace them with more transparent programs.
One such program is the Privacy Sandbox, which is currently in development. Google aims to prevent invasive tracking technologies such as third-party cookies and substitute them with more transparent initiatives.
But is that all? Well, we don’t know at the moment. With GDPR, CPRA, and even other laws getting updated and getting stricter with every iteration, we might get laws that change the tracking scene, like with the iOS 14 update for iPhones, for example.
So everything remains the same now, but here are a few things you might want to consider doing to help mitigate the effects of the depreciation of 3rd party cookies:
First-party data collection: We’ve discussed this in our blog about data types, “Your Comprehensive Guide to First-Party, Second-Party, & Third-Party Data,” but the most important part is that you need to have systems that allow you to collect first-party data to avoid having to rely on third-party data altogether, be it cookies or not.
Consent Management Platforms: While already in place, we definitely need to mention them because now they’re more important than ever, especially with the introduction of an era in privacy is that important.
Server-side Tracking: We have a blog we wrote a while ago about server-side tracking in anticipation of this moment, and so it’s a very helpful resource for you moving forward as everything becomes server-based, even analytics!
Our consultants are here to help you build the right data analytics framework for your needs: contact e-Cens today to learn more.
Implications for advertisers and marketers
1 – Loss of Detailed User Tracking: Third-party cookies have been instrumental in tracking user behavior across multiple websites, which helps in creating detailed user profiles. With their deprecation, advertisers and marketers would lose this level of insight.
2 – Challenges in Remarketing: The deprecation could affect remarketing strategies, as these often rely on third-party cookies to track users’ interactions with a brand across different platforms.
3 – Measurement and Attribution Will Suffer: Third-party cookies are crucial in attributing conversions to the right marketing channels. Their loss could lead to difficulty in accurately measuring various marketing efforts’ effectiveness.
4 – Increased Focus on First-Party Data: As third-party data becomes less accessible, there will be an increased focus on first-party data collection. This will necessitate a shift toward more direct engagement with consumers.
5 – Need for New Technologies and Strategies: The industry will need to innovate and adapt new technologies or strategies for targeted advertising, like Google’s Privacy Sandbox or alternative identifiers like Unified ID 2.0.




